
The “Silent Killer” ~30%
of Americans Don’t
Know They Have10,11
What is PAD?10
Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) occurs when cholesterol and other fats circulating in the blood collect inside the walls of the arteries that supply blood to the limbs. This buildup, referred to as fatty plaque, narrows arteries and can lead to reduced or blocked blood flow (atherosclerosis).
PAD most commonly occurs in the legs but can also be present in the arteries that carry blood from the heart to the head, arms, kidneys, and stomach.1
What are societies saying about PAD Testing and Diagnosing?
Leading health organizations and initiatives are increasingly emphasizing the importance of PAD testing as a critical component of cardiovascular care.
Read below to learn more about these organizations.
American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology
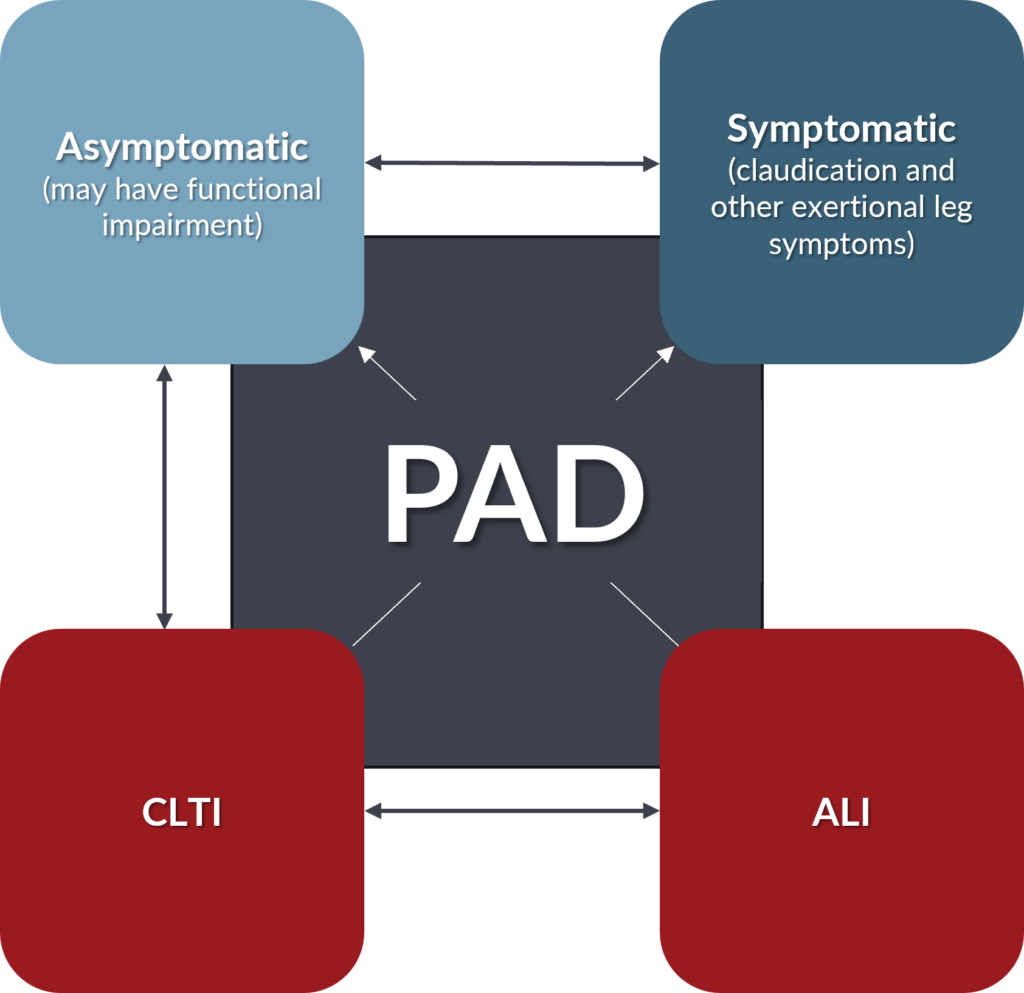
The new 2024 AHA/ACC guidelines emphasize that the standard of care for vascular assessment in patients at risk for PAD include early and routine screening to ensure timely detection and management of disease.
- Age <50 years
- With diabetes mellitus and
- One additional risk factor for atherosclerosis (e.g., history of smoking)
- Age 50 – 64 years
- With risk factors for atherosclerosis
- Family history of PAD
- Chronic kidney disease
- Age ≥65 years
- Known atherosclerotic disease in other vascular beds2
American Diabetes Association

Did You Know?
Patients with diabetes are at an increased risk of arterial calcification.
- Type 1 Diabetes: Calcifications are more commonly found in the coronary and carotid arteries.5
- Type 2 Diabetes: Calcifications tend to occur more frequently across various arterial regions.4
This highlights the importance of regular vascular assessments for individuals with diabetes to prevent complications.
- Perform PAD testing for asymptomatic individuals with diabetes and any of the following:
- ≥ 50 years of age
- Presence of microvascular disease (e.g., retina, kidney, etc.)
- Foot complications
- Any end-organ damage from diabetes
- Consider testing for PAD in patients with diabetes for 10 or more years3
PAD National Action Plan

PAD prevalence is expected to triple over the next 30 years in the U.S. alone.6 The PAD National Action Plan was developed by 25 organizations and over 50 volunteers to provide a framework of six strategic goals to combat this frightening trend.
- Public Awareness: Raising awareness of PAD to improve early detection and prevention.
- Professional Education: Equipping healthcare professionals with the knowledge and tools to effectively diagnose and treat PAD.
- Detection & Treatment: Enhancing screening processes and treatment options to better manage PAD and reduce complications.
- Public Health: Integrating PAD Prevention and management into broader public health initiatives.
- Research: Advancing research efforts to uncover new insights and improve outcomes for PAD patients.
- Advocacy Engagement: Mobilizing advocates to influence policy changes and secure resources for PAD prevention and care.7
How can you contribute to this vital mission?
PAD Pulse Alliance
In response to increasing amputations and a large knowledge gap, the Get a Pulse on PAD campaign is raising public awareness to change this trend.
As healthcare providers, you can empower your patients by:
- Using the educational toolkit
- Teaching patients to advocate for their health by understanding risk factors, symptoms and knowing what questions to ask during visits.8
Veterans Health Administration – PAVE Program
VHA Directive 1410 Transmittal Sheet June 30, 20229
Prevention of Amputations in Veterans Everywhere (PAVE)
- This VHA policy mandates the PAVE program in all VA medical facilities to prevent non-traumatic amputation in Veterans; must implement within 6 months of opening
- An initial foot check is conducted for at-risk populations, with suspicious findings referred to podiatrists for further assessment and determination of amputation risk
- Timely and appropriate referrals and follow-up
- Refer Veterans with amputations to a peer support program, if needed
- Develop a system to identify and track Veterans with amputation or at risk for amputation across all care levels

